HPV and condyloma or genital warts
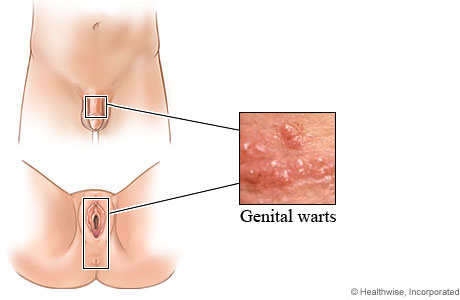 Condyloma are genital warts. They are a manifestation of HPV (Human Papilloma Virus). More than 10% of adults will have condyloma in their lifetime. More than 60% of adults will develop symptoms within 2-3 years of exposures
Condyloma are genital warts. They are a manifestation of HPV (Human Papilloma Virus). More than 10% of adults will have condyloma in their lifetime. More than 60% of adults will develop symptoms within 2-3 years of exposures
HPV 6 and 11 are associated with 90% of genital warts and are rarely associated with cancers. HPV 16 and 18 are high risk HPV subtypes because they are associated with 77% of cervical cancer in woman, 40% of vaginal or vulvar cancer and 90 % of anal cancer.
HPV infection is the most frequent sexually transmitted infection. Condom use is not a sufficient protection as HPV are transmitted via infected secretions through direct skin-to-skin contact during oral, genital, or anal sex with an infected partner with or without penetration. Even in the absence of clinical manifestation, the infected individual may be contagious.
The incubation period may be 1 to 8 months although it can be much longer. Condyloma will disappear within 4 months in 50% of affected individuals. Shape and color of Condyloma will vary depending on location. Condyloma are most frequently found on the penis, scrotum, vulva, perinea and around the anus. Rarely are they found on the cervix or in the vagina.
Neither the PAP smear nor the high risk HPV testing on cervical sampling are screening tests for HPV. Therefore a normal PAP smear does not mean a woman is free from the HPV subtypes that provoke genital warts or that she is not contagious.
A vaccine (Gardasil) is available and protects from HPV 6,11,16 and 18 subtypes. The vaccine is recommended for males and females from ages 9-26 or anyone sexually active and not involved in a committed exclusive long term relationship.
As of now, there is no screening test for HPV for individuals infected by the virus and who are without lesions. STD (STI) screening tests do not look specifically for HPV.
To be vaccinated against HPV and genital warts, make an appointment or contact Crea-MeD at 514‑345‑1356 or email info@crea‑med.ca